ASC-J9
ASC-J9
¥1200
1EA
起订
上海 更新日期:2026-02-15
产品详情:
- 英文名称:
- ASC-J9
- 规格:
- 10mM (in 1mL DMSO)/5mg/10mg/50mg
- 货号:
- A3190
公司简介
| 成立日期 | (14年) |
| 注册资本 | 1500万人民币 |
| 员工人数 | |
| 年营业额 | |
| 经营模式 | |
| 主营行业 |
ASC-J9相关厂家报价
-
- ASC-J9
- 上海嵘崴达实业有限公司
- 2026-02-15
- ¥7533
-

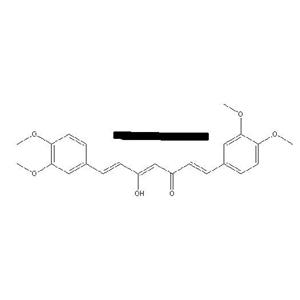
- (1E,4E,6E)-1,7-双(3,4-二甲氧基苯基)-5-羟基-1,4,6-庚三烯-3-酮
- 爱必信(上海)生物科技有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-10
- 询价
-

- (1E,4E,6E)-1,7-双(3,4-二甲氧基苯基)-5-羟基-1,4,6-庚三烯-3-酮
- 纯创(武汉)科技有限公司 VIP
- 2025-12-11
- 询价
-

- (1E,4E,6E)-1,7-双(3,4-二甲氧基苯基)-5-羟基-1,4,6-庚三烯-3-酮
- Alchem Pharmtech,Inc.
- 2022-10-22
- 询价
-

- (1E,4E,6E)-1,7-双(3,4-二甲氧基苯基)-5-羟基-1,4,6-庚三烯-3-酮
- 上海前衍生物科技有限公司
- 2022-10-22
- 询价
-
- ASC-J9
- 台州科鼎化工有限公司
- 2022-05-27
- 询价


