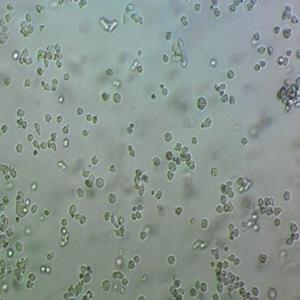
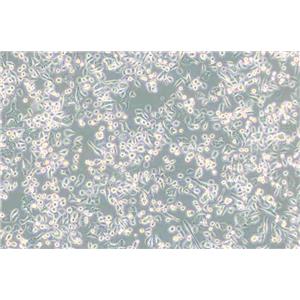
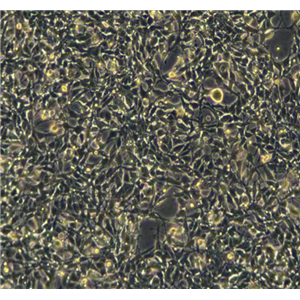
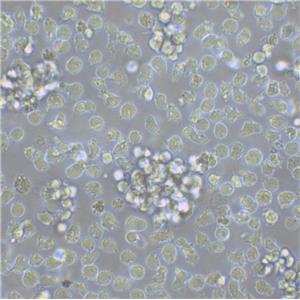
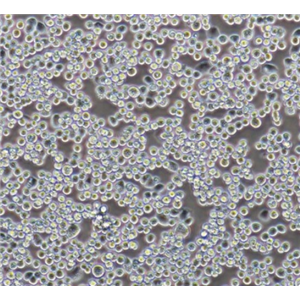
"AsPC-1人转移胰腺腺癌细胞代次低|培养基|送STR图谱
传代比例:1:2-1:4(首次传代建议1:2)
生长特性:贴壁生长
当T25瓶复苏细胞收到货时,请观察好细胞状态后,将T25细胞瓶壁进行75%酒精消毒,将T25瓶置于37度培养箱放置2-4h,以便稳定细胞状态,当细胞密度达80%-90%,即可进行首次传代培养;干冰运输的细胞冻存管收到货后,需立即转入液氮保存或直接进行复苏(第三天换液并检查复苏细胞密度,以便进行下一步)。 能够在实验室条件下进行大量培养和繁殖。这种细胞系在分子生物学和生物技术研究中十分常用。
换液周期:每周2-3次
HPaSteC(HPSC) Cells;背景说明:胰腺星状 Cells;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:C3H-10T1/2细胞、MyLa 2059细胞、HEL-92细胞
WM-239A Cells;背景说明:黑色素瘤;女性;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:KYSE 410细胞、BRL-3A细胞、Mel-624细胞
LMH Cells;背景说明:肝癌;雄性;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:SAOS 2细胞、Madin-Darby Canine Kidney细胞、NCI-H920细胞
AsPC-1人转移胰腺腺癌细胞代次低|培养基|送STR图谱
背景信息:该细胞来源于人胰腺癌裸鼠异种移植产生的癌性腹水,可以表达A,人胰腺相关抗原、人胰腺特异性抗原和黏蛋白。
┈订┈购(技术服务)┈热┈线:1┈3┈6┈4┈1┈9┈3┈0┈7┈9┈1【微信同号】┈Q┈Q:3┈1┈8┈0┈8┈0┈7┈3┈2┈4;
DSMZ菌株保藏中心成立于1969年,是德国的国家菌种保藏中心。该中心一直致力于细菌、真菌、质粒、抗菌素、人体和动物细胞、植物病毒等的分类、鉴定和保藏工作。DSMZ菌种保藏中心是欧洲规模最大的生物资源中心,保藏有动物细胞500多株。Riken BRC成立于1920年,是英国的国家菌种保藏中心。该中心一直致力于细菌、真菌、植物病毒等的分类、鉴定和保藏工作。日本Riken BRC(Riken生物资源保藏中心)是全球三大典型培养物收集中心之一。Riken保藏中心提供了很多细胞系。在世界范围内,这些细胞系,都在医学、科学和兽医中具有重要意义。Riken生物资源中心支持了各种学术、健康、食品和兽医机构的研究工作,并在世界各地不同组织的微生物实验室和研究机构中使用。
产品包装:复苏发货:T25培养瓶(一瓶)或冻存发货:1ml冻存管(两支)
来源说明:细胞主要来源ATCC、ECACC、DSMZ、RIKEN等细胞库
AsPC-1人转移胰腺腺癌细胞代次低|培养基|送STR图谱
物种来源:人源、鼠源等其它物种来源
CL 1-0 Cells;背景说明:肺癌;男性;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:HFT-8810细胞、U373-MG细胞、NCI-H292细胞
Turbot Embryonic Cell line Cells;背景说明:胸腺;上皮 Cells;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:RAOEC细胞、SKNEP细胞、Caco-2/BBe细胞
GM03320D Cells;背景说明:该细胞是1967年4月由NicholsWW,LeeJ和DwightS建立,来源于一名13月龄白人男婴腹部肿块,临床诊断为神经母细胞瘤,伴有极少部位的类器官样分化。;传代方法:1:2传代;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:存在两种细胞类型,小的神经母细胞样细胞和大的透明成纤维样细胞;相关产品有:TK.10细胞、HLEB3细胞、RH35细胞
526 mel Cells;背景说明:黑色素瘤;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:RTE细胞、293-EBNA细胞、Biologics Standards-Cercopithecus-1细胞
┈订┈购(技术服务)┈热┈线:1┈3┈6┈4┈1┈9┈3┈0┈7┈9┈1【微信同号】┈Q┈Q:3┈1┈8┈0┈8┈0┈7┈3┈2┈4;
形态特性:上皮细胞样
细胞冻存复苏材料与方法步骤:常用的细胞冷冻贮存器为贮存器,规格有35L和50L两种。使用时要注意以下几点:(1)一般两周需充一次,至少一个月充一次。温度达-196℃,使用时注意勿让溅到皮肤上,以免引起冻伤。(2)容器为双层结构,中间为真空层,瓶口有双层焊接处,应防止焊接部裂开。(3)在装入时,要注意缓慢小心,并用厚纸卷筒或制漏斗作引导,使直达瓶底,如有专用灌注装置则更HAO。若为初次使用,加时更要缓慢,以免温度骤降而使容器损坏。细胞冻存时常备的材料有:0.25%胰蛋白酶,含10%~20%的血清培养,DMSO(分析纯)或无色新鲜甘油(121°C蒸气GAO压消毒),2mL安瓿(或专用细胞冻存管)、吸管、离心管、喷灯、纱布袋(或冻存管架)等。主要操作步骤为:(1)选择处于对数生长期的细胞,在冻存前一天ZuiHAO换。将多个培养瓶中的细胞培养 去掉,用0.25%胰蛋白酶消化。适时去掉胰蛋白酶,加入少量新培养。用吸管吸取培养反复吹打瓶壁上的细胞,使其成为均匀分散的细胞悬。悬浮生产细胞则不要消化处理。然后将细胞收集于离心管中离心(1000r/min,10分钟)。(2)去上清,加入含20%小牛血清的完全培养基,于4℃预冷15分钟后,逐滴加入已无菌的DMSO或甘油,用吸管轻轻吹打使细胞均匀,细胞浓度为3×106~1×107/mL之间。(3)将上述细胞分装于安瓿或专用冷冻塑料管中,安瓿装1~1.5mL在火焰喷灯上封口,封口处要完全封闭,圆滑无勾。冷冻管要将盖子盖紧,并标记HAO细胞名称和冻存日期,同时作HAO登记(日期、细胞种类及代次、冻存支数)。(4)将装HAO细胞的安瓿或冻存管装入沙布袋内;置于容器颈口处存放过夜,次日转入中。采用控制降温速度的方法也可采用下列步骤:先将安瓿置入4℃冰箱中2~3小时,再移至冰箱冷冻室内3~4小时,再吊入容器颈气态部分存放2小时,Zui后沉入中。细胞冻存在中可以长期保存,但为妥善起见,冻存半年后,ZuiHAO取出一只安瓿细胞复苏培养,观察生长情况,然后再继续冻存。
CHL-IU Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁或悬浮,详见产品说明书部分;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:KU-812-F细胞、SK-BR3细胞、QGY-7703细胞
Centre Antoine Lacassagne-33 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁或悬浮,详见产品说明书部分;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:Det. 562细胞、MV522细胞、MAC1细胞
H.Ep. #2 Cells;背景说明:最初认为这个细胞源自喉上皮癌,但随后通过同功酶分析、HeLa标记染色体和DNA指纹分析发现,起源细胞已被HeLa污染。 角蛋白免疫过氧化物酶染色阳性。;传代方法:1:2传代;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:上皮细胞样;相关产品有:H1792细胞、Hs 739.T细胞、COV-362细胞
Jiyoye (P-2003) Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:每周2-3次。;生长特性:悬浮生长;形态特性:淋巴母细胞;相关产品有:H-1299细胞、COS1细胞、HMCB细胞
BOWES Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:6—1:10传代,2天换液1次;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:上皮细胞;相关产品有:T 24细胞、MDA 435细胞、3T3-A31细胞
Toledo Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:每2-3天换液;生长特性:悬浮生长 ;形态特性:淋巴母细胞样;相关产品有:G-361细胞、H-295细胞、KP4细胞
QBC939 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2传代;生长特性:贴壁生长 ;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:HRA-19细胞、TE9细胞、C518细胞
LICR-HN6 Cells;背景说明:舌鳞癌;男性;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:NK10a细胞、MD Anderson-Metastatic Breast-468细胞、T-ALL 1细胞
MHCC 97 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁或悬浮,详见产品说明书部分;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:LL2细胞、EL-4细胞、MDA-kb2细胞
G 401 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:6传代,每周2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:上皮细胞样;相关产品有:PC-9细胞、HO8910细胞、HEB细胞
PLMVEC Cells;背景说明:肺微血管;内皮 Cells;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:JB6 clone 30, subclone 7b细胞、HTh-74细胞、L(TK-)细胞
NCI-H2108 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁或悬浮,详见产品说明书部分;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:COLO 684细胞、D6P2T细胞、University of Arizona Cell Culture-893细胞
MDA MB231 Cells;背景说明:MDA-MB-231来自患有转移乳腺腺癌的51岁女病人的胸水。在裸鼠和ALS处理的BALB/c小鼠中,它能形成低分化腺癌(III级)。;传代方法:消化3-5分钟,1:2,3天内可长满;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:上皮样;相关产品有:GS-9L细胞、T-ALL1细胞、KMST-6细胞
HECV Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁或悬浮,详见产品说明书部分;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:CCD 19Lu细胞、NCTC 3960细胞、PANC-28细胞
SUNE1 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁或悬浮,详见产品说明书部分;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:GM06141B细胞、NCIH1930细胞、NCIH446细胞
DMS 79 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:4传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:悬浮生长;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:SH-SY5Y Parental细胞、Cates-1B细胞、HN6细胞
Ramos 2G6.4C10 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法: 维持细胞浓度在2×105/ml-1×106/ml;根据细胞浓度每2-3天补液1次。;生长特性:悬浮生长 ;形态特性:淋巴母细胞样;相关产品有:NSI/1-Ag4-1细胞、Hx147细胞、no.11细胞
Abcam HCT 116 EP300 KO Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
AG06239 Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
BayGenomics ES cell line CSI556 Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
BayGenomics ES cell line RST665 Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
BIHi017-A Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
Chula5.hES Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
DA03187 Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
DLD-1 clone A Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
GM03037 Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
P3HRI Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:每2-3天换液;生长特性:悬浮生长 ;形态特性:淋巴母细胞样;相关产品有:SCL I细胞、CCF-STTG1细胞、MDST8细胞
AsPC-1人转移胰腺腺癌细胞代次低|培养基|送STR图谱
SKBr3 Cells;背景说明:这株细胞源自胸水。没有病毒颗粒。亚显微结构特征包括微丝和桥粒,肝糖原颗粒,大溶酶体,成束的细胞质纤丝。SK-BR-3细胞株过表达HER2/c-erb-2基因产物。;传代方法:消化3-5分钟,1:2,3天内可长满;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:上皮样;相关产品有:Hs-281-T细胞、HFTF细胞、OAW 42细胞
BE(2)C Cells;背景说明:神经母细胞瘤;骨髓转移;男性;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:SUM 149PT细胞、NT2/D1细胞、BALB/c 3T3 clone A31细胞
RGC-5 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2传代;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:B16F0细胞、Human Epidermoid carcinoma #2细胞、A 72细胞
J 82 Cells;背景说明:电子显微镜下未观察到桥粒但观察到数目不同的粗面内质网和突出微丝。 含ras (H-ras)癌基因。;传代方法:1:2传代;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:上皮细胞样;相关产品有:RK-13细胞、MNNG-HOS (TE 85, clone F-5)细胞、REC细胞
PLC-PRF-5 Cells;背景说明:该细胞系分泌乙肝病毒表面抗原(HBsAg)。 此细胞系原先被支原体污染,后用BM-cycline去除支原体;传代方法:1:2传代;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:上皮样;相关产品有:NCIH345细胞、DU 4475细胞、207细胞
56.4H7 Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
YES2 Cells;背景说明:食管鳞癌;男性;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:MDAMB175细胞、WM2664细胞、H-295R细胞
Malme-3 M Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:4传代,2天换液1次。;生长特性:混合生长;形态特性:成纤维细胞;相关产品有:KNS-62细胞、NS1-Ag 4/1细胞、SRS-82细胞
Adeno 293 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2传代;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:COLO-824细胞、Hep-G2/C3A细胞、HCAEC细胞
A 172 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁或悬浮,详见产品说明书部分;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:A427细胞、BEAS2B细胞、Tissue Culture-1细胞
CSQT-2 Cells;背景说明:肝癌;男性;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:Blotchy fibroblast-11细胞、COR-L88细胞、BT-474细胞
H1650 Cells;背景说明:该细胞是从一名27岁白人男性(10年烟龄)支气管肺泡癌患者的胸腔积液中分离得到的。;传代方法:1:4-1:6传代;2-3天换液1次。;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:上皮细胞样;相关产品有:H2171细胞、PLB-985细胞、HCCLM6细胞
H1650 Cells;背景说明:该细胞是从一名27岁白人男性(10年烟龄)支气管肺泡癌患者的胸腔积液中分离得到的。;传代方法:1:4-1:6传代;2-3天换液1次。;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:上皮细胞样;相关产品有:H2171细胞、PLB-985细胞、HCCLM6细胞
MCF 7B Cells;背景说明:浸润性导管癌;胸腔积液转移;女性;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:J-111细胞、CCD 1112SK细胞、Hep 2细胞
GM20891 Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
HAP1 KIF15 (-) 1 Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
SK-RC-20 Cells;背景说明:肾癌;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:CT 26细胞、L 1210细胞、TE 32.T细胞
HCC-1833 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁或悬浮,详见产品说明书部分;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:Menschliche Und Tierische Zellkulture-1细胞、Panc 5.04细胞、HOCF细胞
BpRcl Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:4-1:6传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:上皮细胞样;相关产品有:HTR-8/SV neo细胞、NCI-H508细胞、ARH 77细胞
OCI-AML4 Cells;背景说明:急性髓系白血病;女性;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:悬浮;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:HCC-94细胞、F36P细胞、Colo320细胞
373 MG Cells;背景说明:胶质瘤;男性;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:OEC19细胞、MAVER1细胞、NCIH295R细胞
H2452 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:消化3-5分钟。1:2。3天内可长满。;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:上皮样;相关产品有:BrCL12细胞、PTK2细胞、EB2细胞
RA 1 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁或悬浮,详见产品说明书部分;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:NCTC 1469细胞、A549 ATCC细胞、A-704细胞
H.Ep.-2 Cells;背景说明:最初认为这个细胞源自喉上皮癌,但随后通过同功酶分析、HeLa标记染色体和DNA指纹分析发现,起源细胞已被HeLa污染。 角蛋白免疫过氧化物酶染色阳性。;传代方法:1:2传代;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:上皮细胞样;相关产品有:SNU-886细胞、PLA802细胞、BT-B细胞
HPS2973 Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
Jurkat-JMN Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
mDD1 Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
NEYS Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
PUMCHi001-A Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
Ubigene HCT 116 CHD8 KO Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
VRISGi004-A Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
HCT116-SN6 Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
GA-10 clone 4 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:每2-3天换液;生长特性:悬浮生长 ;形态特性:淋巴母细胞样;相关产品有:P388.D1细胞、Hs 636 T细胞、SNU-869细胞
HEC-1-A Cells;背景说明:这株细胞及其亚株HEC-1-B是H.Kuramoto及其同事1968年从一位IA期子宫内膜癌患者身上分离得到的。PAF可以诱导其c-fos的表达。;传代方法:消化3-5分钟,1:2,3天内可长满;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:上皮样;相关产品有:WSU-DLCL2细胞、U-87 MG细胞、Ramos.2G6.4C10细胞
mRMEC Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁或悬浮,详见产品说明书部分;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:A375mel细胞、SCL-II细胞、SK-GT-2细胞
SNU-886 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2传代;生长特性:贴壁或悬浮,详见产品说明书部分;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:SuDHL 2细胞、RBL 1细胞、MIN-6细胞
NOZC-1 Cells;背景说明:患者有癌性腹膜炎。细胞为中等分化的管状胆囊癌。会分泌AFP和CEA。倍增时间48小时,板植率14-19%。细胞可在裸鼠中成瘤,形态与原发肿瘤相似。;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:上皮细胞样;相关产品有:F442A细胞、MFE-280细胞、Hs 636.T细胞
K562/ADR Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁或悬浮,详见产品说明书部分;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:LCMS细胞、PG-4细胞、HSC-I细胞
Rat Fetal Lung-6 Cells;背景说明:胚肺;成纤维细胞;SD大鼠;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:JB6 [Mouse]细胞、HUV-EC-C细胞、SK-MEL-2细胞
H4-II-EC3 Cells;背景说明:在糖皮质激素、胰岛素或cAMP衍生物的诱导下可以产生酪酸基转移酶;可被逆转录病毒感染;可产生白蛋白、转铁蛋白、凝血酶原;在AxC大鼠中可以成瘤。;传代方法:1:2传代;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:上皮样;相关产品有:SUM-190细胞、SKRC-20细胞、T241细胞
OEC33 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2传代;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:上皮样;相关产品有:ZR-75-1细胞、HPF细胞、Wien133细胞
Mv 1 Lu Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁或悬浮,详见产品说明书部分;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:Sf-21细胞、C4-1细胞、RL-65细胞
Jurkat E6-1 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁或悬浮,详见产品说明书部分;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:CLL-CII细胞、Colon-26细胞、HB 611细胞
Karpas-422 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁或悬浮,详见产品说明书部分;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:Colon 38细胞、T.T细胞、Caco-2/ATCC细胞
EM-3 Cells;背景说明:髓系白血病;女性;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:悬浮;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:WERI-Rb-1细胞、SUP T1细胞、CNE-2细胞
L 132 Cells;背景说明:胚肺;女性;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:Roswell Park Memorial Institute 8226细胞、MES-13细胞、H1694细胞
MPP 89 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁或悬浮,详见产品说明书部分;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:KY180细胞、Sp 2/0-Ag 14细胞、INS1细胞
SNUhES46 Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
7860 Cells;背景说明:该细胞源自一位原发性肾透明细胞癌患者。该细胞有微绒毛和桥粒,能在软琼脂上生长。此细胞生成一种PTH(甲状旁腺素)样的多肽,与乳癌和肺癌中生成的肽相似,其N端序列与PTH相似,具有PTH样活性,分子量为6000D。;传代方法:1:2传代;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:上皮样;相关产品有:HPAF II细胞、IMR90细胞、RS411细胞
HIMEC Cells;背景说明:肠微血管内皮 Cells;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:NCI-157细胞、2V6.11细胞、SCL-2细胞
LM3 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2传代;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:上皮样;相关产品有:HCC1500细胞、UCLA-SO-M14细胞、H-35细胞
MT-2 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;生长特性:悬浮生长;形态特性:淋巴母细胞;相关产品有:Stanford University-Diffuse Histiocytic Lymphoma-16细胞、SKNO-1细胞、RPTEC TERT1细胞
MV-522 Cells;背景说明:肺腺癌;女性;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:SUM 102细胞、451-LU细胞、Caki2细胞
Walker 256 Cells;背景说明:乳腺癌;雌性;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:Centre Antoine Lacassagne-85-1细胞、GBC-SD细胞、BHP 10-3细胞
AsPC-1人转移胰腺腺癌细胞代次低|培养基|送STR图谱
Panc 4.03 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2传代;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:上皮样;相关产品有:WEHI-3细胞、RTE细胞、NCI-H2452细胞
SNUC1 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:每3-5天换液。;生长特性:悬浮生长;形态特性:上皮细胞;相关产品有:HSC3细胞、PY8119细胞、AML-EOL-1细胞
CEM-0 Cells;背景说明:G.E. Foley 等人建立了类淋巴母细胞细胞株CCRF-CEM。 细胞是1964年11月从一位四岁白人女性急性淋巴细胞白血病患者的外周血白血球衣中得到。此细胞系从香港收集而来。;传代方法:1:2传代。3天内可长满。;生长特性:悬浮生长;形态特性:淋巴母细胞样;相关产品有:33604细胞、NCIH1341细胞、NB1-RGB细胞
3T3 L1 Cells;背景说明:3T3-L1是从3T3细胞(Swissalbino)中经克隆分离得到的连续传代的亚系。该细胞从快速分裂到汇合和接触性抑制状态经历了前脂肪细胞到脂肪样细胞的转变。该细胞鼠痘病毒阴性;可产生甘油三酯,高浓度血清可增强细胞内脂肪堆积。;传代方法:1:2传代;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:成纤维细胞样;相关产品有:NL20SV细胞、2008细胞、H2286细胞
NG-108-15 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁或悬浮,详见产品说明书部分;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:TC-1 [Mouse lung]细胞、CAL62细胞、Primary Liver Carcinoma/Poliomyelitis Research Foundation/5细胞
SKM1 Cells;背景说明:详见相关文献介绍;传代方法:1:2传代;;生长特性:贴壁生长;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:QBC-939细胞、LS-411N细胞、L-6 myoblast细胞
CAL 148 Cells;背景说明:乳腺癌;胸腔积液转移;女性;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:HCT GEO细胞、Detroit-562细胞、SaOS细胞
Huh7.5 Cells;背景说明:肝癌;男性;传代方法:1:2-1:3传代;每周换液2-3次。;生长特性:贴壁;形态特性:详见产品说明书;相关产品有:Simpson细胞、Vx-2细胞、HSF细胞
BayGenomics ES cell line RRK260 Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
BayGenomics ES cell line XL978 Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
GLUTag Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
OLF10.1.8 Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
1.1B4 Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
MCW073i-40000527 Cells(提供STR鉴定图谱)
" "PubMed=1764370; DOI=10.1038/bjc.1991.467; PMCID=PMC1977874
Barton C.M., Staddon S.L., Hughes C.M., Hall P.A., O'Sullivan C., Kloppel G., Theis B., Russell R.C.G., Neoptolemos J., Williamson R.C.N., Lane D.P., Lemoine N.R.
Abnormalities of the p53 tumour suppressor gene in human pancreatic cancer.
Br. J. Cancer 64:1076-1082(1991)
PubMed=1630814
Ruggeri B.A., Zhang S.-Y., Caamano J., DiRado M., Flynn S.D., Klein-Szanto A.J.P.
Human pancreatic carcinomas and cell lines reveal frequent and multiple alterations in the p53 and Rb-1 tumor-suppressor genes.
Oncogene 7:1503-1511(1992)
PubMed=7972006; DOI=10.1073/pnas.91.23.11045; PMCID=PMC45163
Okamoto A., Demetrick D.J., Spillare E.A., Hagiwara K., Hussain S.P., Bennett W.P., Forrester K., Gerwin B.I., Serrano M., Beach D.H., Harris C.C.
Mutations and altered expression of p16INK4 in human cancer.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91:11045-11049(1994)
PubMed=8026879; DOI=10.1002/ijc.2910580207
Berrozpe G., Schaeffer J., Peinado M.A., Real F.X., Perucho M.
Comparative analysis of mutations in the p53 and K-ras genes in pancreatic cancer.
Int. J. Cancer 58:185-191(1994)
PubMed=8194712; DOI=10.1016/0016-5085(94)90422-7
Simon B., Weinel R., Hohne M., Watz J., Schmidt J., Kortner G., Arnold R.
Frequent alterations of the tumor suppressor genes p53 and DCC in human pancreatic carcinoma.
Gastroenterology 106:1645-1651(1994)
PubMed=8286197; DOI=10.1038/bjc.1994.24; PMCID=PMC1968784
Lohr J.-M., Trautmann B., Gottler M., Peters S., Zauner I., Maillet B., Kloppel G.
Human ductal adenocarcinomas of the pancreas express extracellular matrix proteins.
Br. J. Cancer 69:144-151(1994)
PubMed=21607521; DOI=10.3892/or.1.6.1223
Iguchi H., Morita R., Yasuda D., Takayanagi R., Ikeda Y., Takada Y., Shimazoe T., Nawata H., Kono A.
Alterations of the p53 tumor-suppressor gene and ki-ras oncogene in human pancreatic cancer-derived cell-lines with different metastatic potential.
Oncol. Rep. 1:1223-1227(1994)
PubMed=9331070
Teng D.H.-F., Perry W.L. 3rd, Hogan J.K., Baumgard M.L., Bell R., Berry S., Davis T., Frank D., Frye C., Hattier T., Hu R., Jammulapati S., Janecki T., Leavitt A., Mitchell J.T., Pero R., Sexton D., Schroeder M., Su P.-H., Swedlund B., Kyriakis J.M., Avruch J., Bartel P., Wong A.K.C., Oliphant A., Thomas A., Skolnick M.H., Tavtigian S.V.
Human mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 as a candidate tumor suppressor.
Cancer Res. 57:4177-4182(1997)
PubMed=9665481; DOI=10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65561-7; PMCID=PMC1852940
Paciucci R., Vila M.R., Adell T., Diaz V.M., Tora M., Nakamura T., Real F.X.
Activation of the urokinase plasminogen activator/urokinase plasminogen activator receptor system and redistribution of E-cadherin are associated with hepatocyte growth factor-induced motility of pancreas tumor cells overexpressing Met.
Am. J. Pathol. 153:201-212(1998)
PubMed=10027410; DOI=10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65298-4; PMCID=PMC1850008
Ghadimi B.M., Schrock E., Walker R.L., Wangsa D., Jauho A., Meltzer P.S., Ried T.
Specific chromosomal aberrations and amplification of the AIB1 nuclear receptor coactivator gene in pancreatic carcinomas.
Am. J. Pathol. 154:525-536(1999)
PubMed=10408907; DOI=10.1016/S0304-3835(98)00380-2
Bartsch D.K., Barth P., Bastian D., Ramaswamy A., Gerdes B., Chaloupka B., Deiss Y., Simon B., Schudy A.
Higher frequency of DPC4/Smad4 alterations in pancreatic cancer cell lines than in primary pancreatic adenocarcinomas.
Cancer Lett. 139:43-49(1999)
PubMed=11115575; DOI=10.3892/or.8.1.89
Sun C.-L., Yamato T., Furukawa T., Ohnishi Y., Kijima H., Horii A.
Characterization of the mutations of the K-ras, p53, p16, and SMAD4 genes in 15 human pancreatic cancer cell lines.
Oncol. Rep. 8:89-92(2001)
PubMed=11169959; DOI=10.1002/1097-0215(200002)9999:9999<::AID-IJC1049>3.0.CO;2-C
Sirivatanauksorn V., Sirivatanauksorn Y., Gorman P.A., Davidson J.M., Sheer D., Moore P.S., Scarpa A., Edwards P.A.W., Lemoine N.R.
Non-random chromosomal rearrangements in pancreatic cancer cell lines identified by spectral karyotyping.
Int. J. Cancer 91:350-358(2001)
PubMed=11787853; DOI=10.1007/s004280100474
Moore P.S., Sipos B., Orlandini S., Sorio C., Real F.X., Lemoine N.R., Gress T.M., Bassi C., Kloppel G., Kalthoff H., Ungefroren H., Lohr J.-M., Scarpa A.
Genetic profile of 22 pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Analysis of K-ras, p53, p16 and DPC4/Smad4.
Virchows Arch. 439:798-802(2001)
PubMed=12692724; DOI=10.1007/s00428-003-0784-4
Sipos B., Moser S., Kalthoff H., Torok V., Lohr J.-M., Kloppel G.
A comprehensive characterization of pancreatic ductal carcinoma cell lines: towards the establishment of an in vitro research platform.
Virchows Arch. 442:444-452(2003)
PubMed=14695172
Iacobuzio-Donahue C.A., Ashfaq R., Maitra A., Adsay N.V., Shen-Ong G.L.-C., Berg K., Hollingsworth M.A., Cameron J.L., Yeo C.J., Kern S.E., Goggins M.G., Hruban R.H.
Highly expressed genes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas: a comprehensive characterization and comparison of the transcription profiles obtained from three major technologies.
Cancer Res. 63:8614-8622(2003)
PubMed=15126341; DOI=10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-3159
Heidenblad M., Schoenmakers E.F.P.M., Jonson T., Gorunova L., Veltman J.A., van Kessel A.G., Hoglund M.
Genome-wide array-based comparative genomic hybridization reveals multiple amplification targets and novel homozygous deletions in pancreatic carcinoma cell lines.
Cancer Res. 64:3052-3059(2004)
PubMed=15367885; DOI=10.1097/00006676-200410000-00004
Loukopoulos P., Kanetaka K., Takamura M., Shibata T., Sakamoto M., Hirohashi S.
Orthotopic transplantation models of pancreatic adenocarcinoma derived from cell lines and primary tumors and displaying varying metastatic activity.
Pancreas 29:193-203(2004)
PubMed=15688027; DOI=10.1038/sj.onc.1208383
Heidenblad M., Lindgren D., Veltman J.A., Jonson T., Mahlamaki E.H., Gorunova L., van Kessel A.G., Schoenmakers E.F.P.M., Hoglund M.
Microarray analyses reveal strong influence of DNA copy number alterations on the transcriptional patterns in pancreatic cancer: implications for the interpretation of genomic amplifications.
Oncogene 24:1794-1801(2005)
PubMed=15770730; DOI=10.3748/wjg.v11.i10.1521; PMCID=PMC4305696
Ma J.-H., Patrut E., Schmidt J., Knaebel H.-P., Buchler M.W., Marten A.
Synergistic effects of interferon-alpha in combination with chemoradiation on human pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
World J. Gastroenterol. 11:1521-1528(2005)
PubMed=16912165; DOI=10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0721
Calhoun E.S., Hucl T., Gallmeier E., West K.M., Arking D.E., Maitra A., Iacobuzio-Donahue C.A., Chakravarti A., Hruban R.H., Kern S.E.
Identifying allelic loss and homozygous deletions in pancreatic cancer without matched normals using high-density single-nucleotide polymorphism arrays.
Cancer Res. 66:7920-7928(2006)
PubMed=18298655; DOI=10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00289.x; PMCID=PMC3828895
Pilarsky C., Ammerpohl O., Sipos B., Dahl E., Hartmann A., Wellmann A., Braunschweig T., Lohr J.-M., Jesenofsky R., Friess H., Wente M.N., Kristiansen G., Jahnke B., Denz A., Ruckert F., Schackert H.K., Kloppel G., Kalthoff H., Saeger H.-D., Grutzmann R.
Activation of Wnt signalling in stroma from pancreatic cancer identified by gene expression profiling.
J. Cell. Mol. Med. 12:2823-2835(2008)
PubMed=18380791; DOI=10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00779.x; PMCID=PMC11158928
Suzuki A., Shibata T., Shimada Y., Murakami Y., Horii A., Shiratori K., Hirohashi S., Inazawa J., Imoto I.
Identification of SMURF1 as a possible target for 7q21.3-22.1 amplification detected in a pancreatic cancer cell line by in-house array-based comparative genomic hybridization.
Cancer Sci. 99:986-994(2008)
CLPUB00416
Oberlin L.
Treatment of pancreatic carcinoma cell lines in vitro and vivo with a monoclonal antibody against the transferrin receptor.
Thesis VMD (2009); Justus-Liebig-Universitat Giessen; Giessen; Germany
DOI=10.4172/jpb.1000057
Yamada M., Fujii K., Koyama K., Hirohashi S., Kondo T.
The proteomic profile of pancreatic cancer cell lines corresponding to carcinogenesis and metastasis.
J. Proteomics Bioinformatics 2:1-18(2009)
PubMed=20037478; DOI=10.4161/cbt.8.21.9685; PMCID=PMC2824894
Kent O.A., Mullendore M.E., Wentzel E.A., Lopez-Romero P., Tan A.-C., Alvarez H., West K.M., Ochs M.F., Hidalgo M., Arking D.E., Maitra A., Mendell J.T.
A resource for analysis of microRNA expression and function in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells.
Cancer Biol. Ther. 8:2013-2024(2009)
PubMed=20164919; DOI=10.1038/nature08768; PMCID=PMC3145113
Bignell G.R., Greenman C.D., Davies H.R., Butler A.P., Edkins S., Andrews J.M., Buck G., Chen L., Beare D., Latimer C., Widaa S., Hinton J., Fahey C., Fu B.-Y., Swamy S., Dalgliesh G.L., Teh B.T., Deloukas P., Yang F.-T., Campbell P.J., Futreal P.A., Stratton M.R.
Signatures of mutation and selection in the cancer genome.
Nature 463:893-898(2010)
PubMed=20215515; DOI=10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3458; PMCID=PMC2881662
Rothenberg S.M., Mohapatra G., Rivera M.N., Winokur D., Greninger P., Nitta M., Sadow P.M., Sooriyakumar G., Brannigan B.W., Ulman M.J., Perera R.M., Wang R., Tam A., Ma X.-J., Erlander M., Sgroi D.C., Rocco J.W., Lingen M.W., Cohen E.E.W., Louis D.N., Settleman J., Haber D.A.
A genome-wide screen for microdeletions reveals disruption of polarity complex genes in diverse human cancers.
Cancer Res. 70:2158-2164(2010)
PubMed=20418756; DOI=10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181c15963; PMCID=PMC2860631
Deer E.L., Gonzalez-Hernandez J., Coursen J.D., Shea J.E., Ngatia J.G., Scaife C.L., Firpo M.A., Mulvihill S.J.
Phenotype and genotype of pancreatic cancer cell lines.
Pancreas 39:425-435(2010)
PubMed=22460905; DOI=10.1038/nature11003; PMCID=PMC3320027
Barretina J.G., Caponigro G., Stransky N., Venkatesan K., Margolin A.A., Kim S., Wilson C.J., Lehar J., Kryukov G.V., Sonkin D., Reddy A., Liu M., Murray L., Berger M.F., Monahan J.E., Morais P., Meltzer J., Korejwa A., Jane-Valbuena J., Mapa F.A., Thibault J., Bric-Furlong E., Raman P., Shipway A., Engels I.H., Cheng J., Yu G.-Y.K., Yu J.-J., Aspesi P. Jr., de Silva M., Jagtap K., Jones M.D., Wang L., Hatton C., Palescandolo E., Gupta S., Mahan S., Sougnez C., Onofrio R.C., Liefeld T., MacConaill L.E., Winckler W., Reich M., Li N.-X., Mesirov J.P., Gabriel S.B., Getz G., Ardlie K., Chan V., Myer V.E., Weber B.L., Porter J., Warmuth M., Finan P., Harris J.L., Meyerson M.L., Golub T.R., Morrissey M.P., Sellers W.R., Schlegel R., Garraway L.A.
The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia enables predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity.
Nature 483:603-607(2012)
PubMed=22585861; DOI=10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0224; PMCID=PMC5057396
Marcotte R., Brown K.R., Suarez Saiz F.J., Sayad A., Karamboulas K., Krzyzanowski P.M., Sircoulomb F., Medrano M., Fedyshyn Y., Koh J.L.-Y., van Dyk D., Fedyshyn B., Luhova M., Brito G.C., Vizeacoumar F.J., Vizeacoumar F.S., Datti A., Kasimer D., Buzina A., Mero P., Misquitta C., Normand J., Haider M., Ketela T., Wrana J.L., Rottapel R., Neel B.G., Moffat J.
Essential gene profiles in breast, pancreatic, and ovarian cancer cells.
Cancer Discov. 2:172-189(2012)
DOI=10.4172/2324-9293.1000104
Wagenhauser M.U., Ruckert F., Niedergethmann M., Grutzmann R., Saeger H.-D.
Distribution of characteristic mutations in native ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas and pancreatic cancer cell lines.
Cell Biol. Res. Ther. 2:1000104.1-1000104.5(2013)
PubMed=25167228; DOI=10.1038/bjc.2014.475; PMCID=PMC4453732
Hamidi H., Lu M., Chau K., Anderson L., Fejzo M.S., Ginther C., Linnartz R., Zubel A., Slamon D.J., Finn R.S.
KRAS mutational subtype and copy number predict in vitro response of human pancreatic cancer cell lines to MEK inhibition.
Br. J. Cancer 111:1788-1801(2014)
PubMed=25984343; DOI=10.1038/sdata.2014.35; PMCID=PMC4432652
Cowley G.S., Weir B.A., Vazquez F., Tamayo P., Scott J.A., Rusin S., East-Seletsky A., Ali L.D., Gerath W.F.J., Pantel S.E., Lizotte P.H., Jiang G.-Z., Hsiao J., Tsherniak A., Dwinell E., Aoyama S., Okamoto M., Harrington W., Gelfand E.T., Green T.M., Tomko M.J., Gopal S., Wong T.C., Li H.-B., Howell S., Stransky N., Liefeld T., Jang D., Bistline J., Meyers B.H., Armstrong S.A., Anderson K.C., Stegmaier K., Reich M., Pellman D., Boehm J.S., Mesirov J.P., Golub T.R., Root D.E., Hahn W.C.
Parallel genome-scale loss of function screens in 216 cancer cell lines for the identification of context-specific genetic dependencies.
Sci. Data 1:140035-140035(2014)
PubMed=25485619; DOI=10.1038/nbt.3080
Klijn C., Durinck S., Stawiski E.W., Haverty P.M., Jiang Z.-S., Liu H.-B., Degenhardt J., Mayba O., Gnad F., Liu J.-F., Pau G., Reeder J., Cao Y., Mukhyala K., Selvaraj S.K., Yu M.-M., Zynda G.J., Brauer M.J., Wu T.D., Gentleman R.C., Manning G., Yauch R.L., Bourgon R., Stokoe D., Modrusan Z., Neve R.M., de Sauvage F.J., Settleman J., Seshagiri S., Zhang Z.-M.
A comprehensive transcriptional portrait of human cancer cell lines.
Nat. Biotechnol. 33:306-312(2015)
PubMed=25877200; DOI=10.1038/nature14397
Yu M., Selvaraj S.K., Liang-Chu M.M.Y., Aghajani S., Busse M., Yuan J., Lee G., Peale F.V., Klijn C., Bourgon R., Kaminker J.S., Neve R.M.
A resource for cell line authentication, annotation and quality control.
Nature 520:307-311(2015)
PubMed=26216984; DOI=10.1073/pnas.1501605112; PMCID=PMC4538616
Daemen A., Peterson D., Sahu N., McCord R., Du X.-N., Liu B., Kowanetz K., Hong R., Moffat J., Gao M., Boudreau A., Mroue R., Corson L., O'Brien T., Qing J., Sampath D., Merchant M., Yauch R.L., Manning G., Settleman J., Hatzivassiliou G., Evangelista M.
Metabolite profiling stratifies pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas into subtypes with distinct sensitivities to metabolic inhibitors.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112:E4410-E4417(2015)
PubMed=26589293; DOI=10.1186/s13073-015-0240-5; PMCID=PMC4653878
Scholtalbers J., Boegel S., Bukur T., Byl M., Goerges S., Sorn P., Loewer M., Sahin U., Castle J.C.
TCLP: an online cancer cell line catalogue integrating HLA type, predicted neo-epitopes, virus and gene expression.
Genome Med. 7:118.1-118.7(2015)
PubMed=26586397; DOI=10.1007/s13277-015-4405-z
Zhang J., Wang D.-M., Hu N., Wang Q., Yu S., Wang J.
The construction and proliferative effects of a lentiviral vector capable of stably overexpressing SPINK1 gene in human pancreatic cancer AsPC-1 cell line.
Tumor Biol. 37:5847-5855(2016)
PubMed=27259358; DOI=10.1074/mcp.M116.058313; PMCID=PMC4974343
Humphrey E.S., Su S.-P., Nagrial A.M., Hochgrafe F., Pajic M., Lehrbach G.M., Parton R.G., Yap A.S., Horvath L.G., Chang D.K., Biankin A.V., Wu J.-M., Daly R.J.
Resolution of novel pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma subtypes by global phosphotyrosine profiling.
Mol. Cell. Proteomics 15:2671-2685(2016)
PubMed=27397505; DOI=10.1016/j.cell.2016.06.017; PMCID=PMC4967469
Iorio F., Knijnenburg T.A., Vis D.J., Bignell G.R., Menden M.P., Schubert M., Aben N., Goncalves E., Barthorpe S., Lightfoot H., Cokelaer T., Greninger P., van Dyk E., Chang H., de Silva H., Heyn H., Deng X.-M., Egan R.K., Liu Q.-S., Miroo T., Mitropoulos X., Richardson L., Wang J.-H., Zhang T.-H., Moran S., Sayols S., Soleimani M., Tamborero D., Lopez-Bigas N., Ross-Macdonald P., Esteller M., Gray N.S., Haber D.A., Stratton M.R., Benes C.H., Wessels L.F.A., Saez-Rodriguez J., McDermott U., Garnett M.J.
A landscape of pharmacogenomic interactions in cancer.
Cell 166:740-754(2016)
PubMed=27910856; DOI=10.1038/cgt.2016.71; PMCID=PMC5159445
Mezencev R., Matyunina L.V., Wagner G.T., McDonald J.F.
Acquired resistance of pancreatic cancer cells to cisplatin is multifactorial with cell context-dependent involvement of resistance genes.
Cancer Gene Ther. 23:446-453(2016)
PubMed=28196595; DOI=10.1016/j.ccell.2017.01.005; PMCID=PMC5501076
Li J., Zhao W., Akbani R., Liu W.-B., Ju Z.-L., Ling S.-Y., Vellano C.P., Roebuck P., Yu Q.-H., Eterovic A.K., Byers L.A., Davies M.A., Deng W.-L., Gopal Y.N.V., Chen G., von Euw E.M., Slamon D.J., Conklin D., Heymach J.V., Gazdar A.F., Minna J.D., Myers J.N., Lu Y.-L., Mills G.B., Liang H.
Characterization of human cancer cell lines by reverse-phase protein arrays.
Cancer Cell 31:225-239(2017)
PubMed=29444439; DOI=10.1016/j.celrep.2018.01.051; PMCID=PMC6343826
Yuan T.L., Amzallag A., Bagni R., Yi M., Afghani S., Burgan W., Fer N., Strathern L.A., Powell K., Smith B., Waters A.M., Drubin D.A., Thomson T., Liao R., Greninger P., Stein G.T., Murchie E., Cortez E., Egan R.K., Procter L., Bess M., Cheng K.T., Lee C.-S., Lee L.C., Fellmann C., Stephens R., Luo J., Lowe S.W., Benes C.H., McCormick F.
Differential effector engagement by oncogenic KRAS.
Cell Rep. 22:1889-1902(2018)
PubMed=30894373; DOI=10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2747; PMCID=PMC6445675
Dutil J., Chen Z.-H., Monteiro A.N.A., Teer J.K., Eschrich S.A.
An interactive resource to probe genetic diversity and estimated ancestry in cancer cell lines.
Cancer Res. 79:1263-1273(2019)
PubMed=30971826; DOI=10.1038/s41586-019-1103-9
Behan F.M., Iorio F., Picco G., Goncalves E., Beaver C.M., Migliardi G., Santos R., Rao Y., Sassi F., Pinnelli M., Ansari R., Harper S., Jackson D.A., McRae R., Pooley R., Wilkinson P., van der Meer D.J., Dow D., Buser-Doepner C.A., Bertotti A., Trusolino L., Stronach E.A., Saez-Rodriguez J., Yusa K., Garnett M.J.
Prioritization of cancer therapeutic targets using CRISPR-Cas9 screens.
Nature 568:511-516(2019)
PubMed=31068700; DOI=10.1038/s41586-019-1186-3; PMCID=PMC6697103
Ghandi M., Huang F.W., Jane-Valbuena J., Kryukov G.V., Lo C.C., McDonald E.R. 3rd, Barretina J.G., Gelfand E.T., Bielski C.M., Li H.-X., Hu K., Andreev-Drakhlin A.Y., Kim J., Hess J.M., Haas B.J., Aguet F., Weir B.A., Rothberg M.V., Paolella B.R., Lawrence M.S., Akbani R., Lu Y.-L., Tiv H.L., Gokhale P.C., de Weck A., Mansour A.A., Oh C., Shih J., Hadi K., Rosen Y., Bistline J., Venkatesan K., Reddy A., Sonkin D., Liu M., Lehar J., Korn J.M., Porter D.A., Jones M.D., Golji J., Caponigro G., Taylor J.E., Dunning C.M., Creech A.L., Warren A.C., McFarland J.M., Zamanighomi M., Kauffmann A., Stransky N., Imielinski M., Maruvka Y.E., Cherniack A.D., Tsherniak A., Vazquez F., Jaffe J.D., Lane A.A., Weinstock D.M., Johannessen C.M., Morrissey M.P., Stegmeier F., Schlegel R., Hahn W.C., Getz G., Mills G.B., Boehm J.S., Golub T.R., Garraway L.A., Sellers W.R.
Next-generation characterization of the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia.
Nature 569:503-508(2019)"