20549-47-7
询价
5kg
起订
香港 更新日期:2024-04-14
产品详情:
- CAS号:
- 20549-47-7
- 纯度规格:
- 98.00%
- 产品类别:
- 特殊材料前驱体
- 无:
- 无
公司简介
N/A
| 成立日期 | (23年) |
| 注册资本 | 340万美元 |
| 员工人数 | 10-50人 |
| 年营业额 | ¥ 300万-500万 |
| 经营模式 | 贸易,工厂,服务 |
| 主营行业 | 中间体,有机原料,医药原料 |
相关厂家报价
-

- 30007-47-7
- 河南阿尔法化工有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-11
- 询价
-

- 1380437-47-7
- 滨海吉尔多肽有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-12
- 询价
-
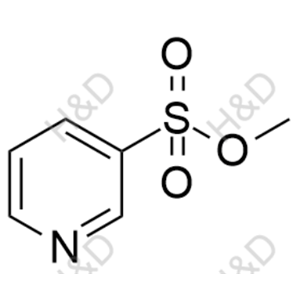
- Vonoprazan Impurity 47 沃诺拉赞杂质47 1421640-34-7
- 深圳市恒丰万达医药科技有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-09
- 询价
-
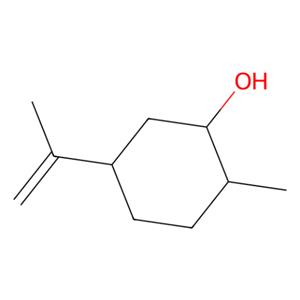
- aladdin 阿拉丁 D485592 (-)-二氢香芹醇 20549-47-7 异构体的混合物,≥95.0%(对映体总量,GC)
- 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司 VIP
- 2025-05-16
- ¥432.90


