| Description | Geranylgeraniol is an orally acitve vitamin K2 sub-type, an intermediate of the mevalonate pathway. Geranylgeraniol targets NF-kB signaling pathway and could alleviate LPS-induced microglial inflammation in animal model[1][2][3][4]. |
|---|
| Related Catalog | Research Areas >> Inflammation/Immunology |
|---|
| Target | NF-kB[1] |
|---|
| In Vitro | Geranylgeraniol (0-10 μM; 24 h) dose-dependently suppresses the LPS-induced increase in the mRNA levels of Il-1β, Tnf-α, Il-6, and Cox-2[1]. Geranylgeraniol (10 μM; 24 h) inhibits the phosphorylation of TAK1, IKKα/β, and NF-κB p65 proteins as well as NF-κB nuclear translocation induced by LPS while maintaining IκBα expression[1]. Geranylgeraniol, (50 μM; 24 h) eliminates cell damage caused by Simvastatin (HY-17502) (10 µM) and Mevalonat (10 mM), and reduces the inflammatory marker and the damage of the mitochondria, maintaining its shape and component[2]. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: MG6 cell Concentration: 0, 1, 10 μM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Suppressed by TAK1, IKKα/β, and NF-κB p65 proteins level at 10 μM. RT-PCR[1] Cell Line: MG6 cell Concentration: 10 μM Incubation Time: 0, 6, 12, 24 hours Result: Significantly inhibited pro-inflammatory cytokine Il-1β, Tnf-α, Il-6, and Cox-2 mRNA level. |
|---|
| In Vivo | Geranylgeraniol (725 mg/kg/d; p.o.; 90 d) is not toxicologically significant with a dose below 725 mg/kg/d in rats[3]. Geranylgeraniol (483 mg/kg/d; p.o.; 10 d) suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation via inhibition of nuclear factor-κB activation in rats[4]. Animal Model: Han Wistar rats (169-192 g for male; 116-152 g for female)[3] Dosage: 0, 725, 1450, and 2900 mg/kg Administration: Oral gavage; once daily; 90 days Result: Showed the lowest observed adverse effect level (LOAEL) for local effects and the no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) for systemic effects as 725 mg/kg/d. Reduced body weights by 12.9 and 21.6% in the intermediate- and high-dose group males, respectively, compared to controls. Animal Model: Wistar rats (male, 8-week-old, 130-150 g)[4] Dosage: 0, 48.3, 483, 4830 mg/kg Administration: Oral gavage; once daily; 10 days; with or not LPS challenge (i.p.; 0.5 mg/kg) Result: Suppressed LPS-induced inflammatory cytokines and mRNA expression of LPS-induced inflammatory genes in liver with doses of 483 mg/kg and 4830 mg/kg. Suppressed protein levels of IRAK1, TRAF6, and TAK1, originating from transcriptional down-regulation with doses of 483 mg/kg and 4830 mg/kg. |
|---|
| References | [1]. Saputra WD, et al. Geranylgeraniol Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in Mouse-Derived MG6 Microglial Cells via NF-κB Signaling Modulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 29;22(19):10543. [2]. Marcuzzi A, et al. Geranylgeraniol and Neurological Impairment: Involvement of Apoptosis and Mitochondrial Morphology. Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Mar 11;17(3):365. [3]. Preece K, et al. A toxicological evaluation of geranylgeraniol. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2021 Aug;124:104975. [4]. Giriwono PE, et al. Dietary supplementation with geranylgeraniol suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation via inhibition of nuclear factor-κB activation in rats. Eur J Nutr. 2013 Apr;52(3):1191-9. |
|---|
 China
China



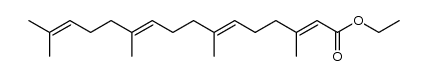
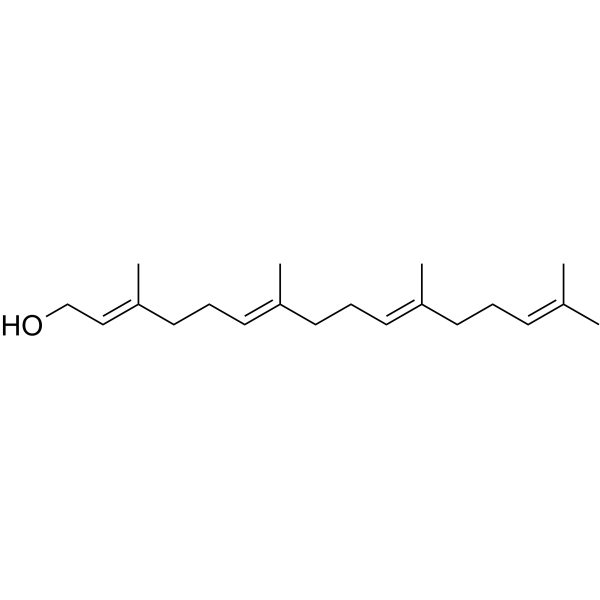

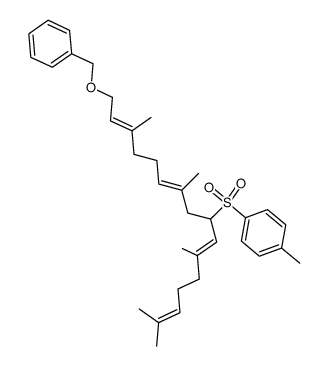 CAS#:68690-51-7
CAS#:68690-51-7 CAS#:71816-56-3
CAS#:71816-56-3 CAS#:24163-93-7
CAS#:24163-93-7![[3-methyl-3-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)oxiran-2-yl]methanol structure](https://www.chemsrc.com/caspic/455/107438-44-8.png) CAS#:107438-44-8
CAS#:107438-44-8 CAS#:142673-23-2
CAS#:142673-23-2 CAS#:504-96-1
CAS#:504-96-1 CAS#:505-32-8
CAS#:505-32-8




