Description
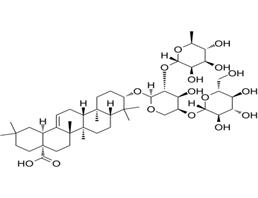
Hederacolchiside A1, isolated from Pulsatilla chinensis, suppresses proliferation of tumor cells by inducing apoptosis through modulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway[1]. Hederacolchiside A1 has antischistosomal activity, affecting parasite viability both in vivo and in vitro[2].
Related Catalog
Signaling Pathways >> PI3K/Akt/mTOR >> mTOR
Signaling Pathways >> Apoptosis >> Apoptosis
Research Areas >> Cancer
Research Areas >> Infection
Signaling Pathways >> PI3K/Akt/mTOR >> PI3K
Signaling Pathways >> PI3K/Akt/mTOR >> Akt
In Vitro
Hederacolchiside A1 reduces the mitochondrial membrane potential and Bcl-2 protein levels, whereas cleaved caspase-3 was higher[1]. Hederacolchiside A1 effectively inhibits the phosphorylations of phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K), protein kinase B (Akt), and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) [1].
In Vivo
hederacolchiside A1 (3.0, 4.5, and 6.0 mg/kg, ip) can significantly inhibit the weight of tumor in an H22 xenograft model[1]. Hederacolchiside A1 (3.25, 7.5, and 15.0 mg/kg, ig) can significantly inhibit the weight of tumor in nude mice xenograft tumor models using human breast carcinoma MCF-7 cells[1].
References
[1]. Yan-Er Wang, et al. Hederacolchiside A1 suppresses proliferation of tumor cells by inducing apoptosis through modulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Chinese Herbal Medicines.Volume 10, Issue 2, April 2018, Pages 215-222
[2]. Kang N, et al. Antischistosomal Properties of Hederacolchiside A1 Isolated from Pulsatilla chinensis. Molecules. 2018 Jun 13;23(6).

 China
China