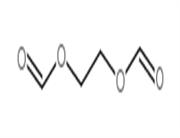
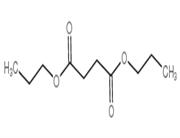
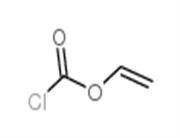
Chemical Properties
Off-White Solid
Uses
A metabolite of Cefpodoxime Proxetil. An antibacterial.
Uses
A metabolite of Cefpodoxime Proxetil (C243860). An antibacterial.
Uses
Cefpodoxime Proxetil metabolite antibiotic
Definition
ChEBI: A third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic with methoxymethyl and (2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetamino substituents at positions 3 and 7, respectively, of the cephem skeleton. Given by mouth as its proxetil ester prodrug, it is used to treat acute otitis media, pharyngitis, and sinusitis.
Brand name
Vantin (Pharmacia & Upjohn).
Antimicrobial activity
It is stable to a wide range of plasmid-mediated β-lactamases. It induces the chromosomal β-lactamases of Ps. aeruginosa, Enterobacter spp., S. marcescens and Citrobacter spp., but is a less potent inducer than cefoxitin.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption: c. 50%
Cmax 200 mg oral: 2.1 mg/L after 3 h
Plasma half-life: c. 2.2 h
Volume of distribution: c. 35 L
Plasma protein binding: 20–30%
Absorption and distribution
The ester is rapidly hydrolyzed to the parent compound in the small intestine. Bioavailability increases to 65% if taken with food, but antacids and H2-receptor antagonists reduce absorption. Unabsorbed drug is hydrolyzed and excreted in the feces.
It is well distributed and penetrates well into tissues (including lung tissue) and inflammatory exudate to achieve concentrations inhibitory to common pathogens.
Metabolism and excretion
The hydrolyzed prodrug is not subject to further metabolism. About 80% of the absorbed compound (30–40% of the original dose) appears in the urine over 24 h. Excretion is by glomerular filtration and tubular secretion; probenecid delays secretion and increases the peak plasma concentration.
Metabolism and excretion
The hydrolyzed prodrug is not subject to further metabolism. About 80% of the absorbed compound (30–40% of the original dose) appears in the urine over 24 h. Excretion is by glomerular filtration and tubular secretion; probenecid delays secretion and increases the peak plasma concentration.
Clinical Use
Cefpodoxime has been used principally for the treatment of upper and lower respiratory tract infections in children and adults.
Side effects
The drug is well tolerated, but gastrointestinal disturbance with diarrhea is common. Pseudomembranous colitis has been reported occasionally. Other side effects are those common to cephalosporins.

 China
China