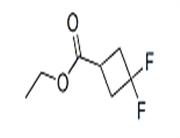
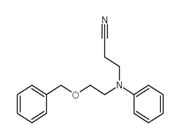
Chemical Properties
Colorless, crystalline solid.
Uses
[3-[[(Phenylamino)carbonyl]oxy]phenyl]carbamic acid ethyl ester is a carbanilate based herbicide used in the weed control programs in sugar beet.
Uses
Selective systemic herbicide used to control broad-leaved weeds such as buckwheat, chickweed, fiddleneck, kochnia, mustard, pigweed and ragweed.
Definition
ChEBI: A carbamate ester that is phenylcarbamic acid in which the hydrogen of the hydroxy group has been replaced by a 3-[(ethoxycarbonyl)amino]phenyl group. It is an agrochemical used as a herbicide.
Potential Exposure
[3-[[(Phenylamino)carbonyl]oxy]phenyl]carbamic acid ethyl ester is a postemergence bis-carbamate herbi- cide used on sugarbeets to control annual weeds such as pigweed, wild mustard, lamb’s quarters, nightshade, chick- weed, buckwheat, goosefoot, ragweed, fiddleneck, and kochia
Environmental Fate
Soil. Degrades in soil forming the intermediate 3-hydroxycarbanilate (Worthing and Hance, 1991). The reported half-lives in soil are 70 days, 20 hours and 10 minutes at pH values of 5, 7 and 9, respectively (Worthing and Hance, 1991).
Plant. In sugar beets, m-aminophenol and ethyl-N-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-carbamate were identified as metabolites (Hartley and Kidd, 1987).
Shipping
UN2757 Carbamate pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Incompatibilities
Esters with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interac- tion of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters with alkali metals and hydrides. Carbamates are incompatible with reducing agents, strong acids, oxidizing acids, peroxides, and bases. Contact with active metals or nitrides cause the release of flammable, and potentially explosive, hydrogen gas. Forms Carbon monoxide and toxic nitrogen oxides when heated to decomposition.
Waste Disposal
Do not discharge into drains or sewers. Dispose of waste material as hazardous waste using a licensed disposal contractor to an approved landfill. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guid- ance on acceptable disposal practices. Incineration with effluent gas scrubbing is recommended. Containers must be disposed of properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.

 China
China



![[3-[[(Phenylamino)carbonyl]oxy]phenyl]carbamic acid ethyl ester](https://img.chemicalbook.com/ProductImageEN/2019-12/Large/38c2d49c-3955-4575-a0ca-1ab0a7203931.jpg)
![[3-[[(Phenylamino)carbonyl]oxy]phenyl]carbamic acid ethyl ester Structure](https://www.chemicalbook.com/CAS/GIF/13684-56-5.gif)