| Description |
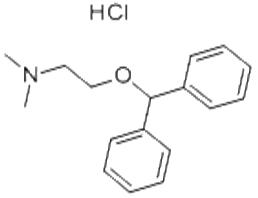
Diphenhydramine hydrochloride is an antihistamine drug having the chemical name 2-(Diphenylmethoxy)- N,N-dimethylethylamine hydrochloride. It occurs as a white, crystalline powder, is freely soluble in water and alcohol and has a molecular weight of 291.82.
The molecular formula is C17H21NO·HCl and the structural formula is as follows:

Diphenhydramine hydrochloride in the parenteral form is a sterile, pyrogen-free solution available in a concentration of 50 mg of diphenhydramine hydrochloride per mL. The solutions for parenteral use have been adjusted to a pH between 5.0 and 6.0 with either sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid and contains 0.1 mg/mL benzethonium chloride as a germicidal agent. |
| Clinical Pharmacology |
Diphenhydramine hydrochloride is an antihistamine with anticholinergic (drying) and sedative side effects. Antihistamines appear to compete with histamine for cell receptor sites on effector cells. Diphenhydramine hydrochloride in the injectable form has a rapid onset of action. Diphenhydramine hydrochloride is widely distributed throughout the body, including the CNS. A portion of the drug is excreted unchanged in the urine, while the rest is metabolized via the liver. Detailed information on the pharmacokinetics of Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride Injection is not available. |
| Indications and Usage |
Diphenhydramine hydrochloride in the injectable form is effective in adults and pediatric patients, other than premature infants and neonates, for the following conditions when diphenhydramine hydrochloride in the oral form is impractical.
- antihistaminic: For amelioration of allergic reactions to blood or plasma, in anaphylaxis as an adjunct to epinephrine and other standard measures after the acute symptoms have been controlled, and for other uncomplicated allergic conditions of the immediate type when oral therapy is impossible or contraindicated.
- Motion Sickness: For active treatment of motion sickness.
- Antiparkinsonism: For use in parkinsonism, when oral therapy is impossible or contraindicated, as follows: parkinsonism in the elderly who are unable to tolerate more potent agents; mild cases of parkinsonism in other age groups, and in other cases of parkinsonism in combination with centrally acting anticholinergic agents.
|
| Drug overdose |
Antihistamine overdosage reactions may vary from central nervous system depression to stimulation. Stimulation is particularly likely in pediatric patients. Atropine-like signs and symptoms; dry mouth; fixed, dilated pupils; flushing; and gastrointestinal symptoms may also occur. Stimulants should not be used. Vasopressors may be used to treat hypotension. |
| Contraindications |
- Use in Neonates or Premature Infants: This drug should not be used in neonates or premature infants.
- Use in Nursing Mothers: Because of the higher risk of antihistamines for infants generally, and for neonates and prematures in particular, antihistamine therapy is contraindicated in nursing mothers.
- Use as a Local Anesthetic: Because of the risk of local necrosis, this drug should not be used as a local anesthetic.
- Antihistamines are also contraindicated in the following conditions: Hyper sensitivity to diphenhydramine hydrochloride and other antihistamines of similar chemical structure.
|
| Chemical Properties |
white crystalline powder |
| Uses |
Diphenhydramine is a H1-histamine receptor antagonist. Diphenhydramine is categorized as an antihistaminic; sedative, hypnotic. |
| Uses |
antihistamine, sedative, treatment of allergic |
| Uses |
A histamine H1-receptor antagonist. |
| Uses |
H1-Histamine receptor antagonist. Antihistaminic; sedative, hypnotic |
| Definition |
ChEBI: The hydrochloride salt of diphenhydramine. |
| General Description |
White or almost-white crystalline powder. Odorless with a bitter numbing taste. pH (5% aqueous solution) 4-6. |
| Air & Water Reactions |
Water soluble. Aqueous solutions are acidic. |
| Reactivity Profile |
N-(2-Diphenylmethoxyethyl)-N,N-dimethylamine hydrochloride gives acidic solutions in water. Neutralizes bases. May react with strong oxidizing and strong reducing agents. May catalyze organic reactions. Slowly darkens on exposure to light. |
| Fire Hazard |
Flash point data for N-(2-Diphenylmethoxyethyl)-N,N-dimethylamine hydrochloride are not available; however, N-(2-Diphenylmethoxyethyl)-N,N-dimethylamine hydrochloride is probably combustible. |
| Biological Activity |
H 1 receptor antagonist. Antihistamine. |

 China
China