Pyrifluquinazon was introduced in Japan in 2007 to control aphids, whiteflies, thrips, mealybugs and scale insects on vegetables and ornamentals. It received U.S. registration for greenhouse use on ornamentals in 2013.
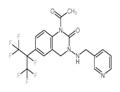
1-Acetyl-3,4-dihydro-3-[(3-pyridinylmethyl)amino]-6-[1,2,2,2-tetrafluoro-1-(trifluoromethyl)ethyl]-2(1H)-quinazolinone is a insecticide.
ChEBI: Pyrifluquinazon is a member of the class of quinazolines that is 3,4-dihydroquinazolin-2-one which is substituted at positions 1, 4, and 6 by acetyl, pyridin-3-ylmethyl, and perfluoroisopropyl groups, respectively. An insecticide used to control sucking and chewing pests by disturbing their coordination and ability to feed. It has a role as an insecticide, a TRPV channel modulator and an agrochemical. It is a member of quinazolines, a member of pyridines, a member of acetamides and an organofluorine compound.
U.S. registration of pyrifluquinazon restricts it to greenhouse use on ornamentals because of its persistence and high toxicity to freshwater invertebrates.
Pyrifluquinazon modifies insect behavior, rapidly stopping feeding such that insects starve to death. It may have the same mode of action as pymetrozine, but this has not yet been determined.