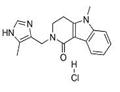
Lotronex (alosetron) was developed for the treatment of severe
irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and was approved for use by
the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2000.
Although Lotronex had a relatively high improvement rate in
patients taking the drug for IBS, it was voluntarily pulled from
the market by GlaxoWellcome that same year due to reports of
severe adverse side effects, some resulting in death.
In 2002, Lotronex was reapproved in a supplemental New
Drug Application for use under more restrictive conditions.
Now with a risk management program to be consulted prior to
administration of the drug, Lotronex is designated to be
prescribed only when its medical benefits outweigh the risks of
toxic effects; women with severe diarrhea-predominant IBS are
now the focal point of prescriptions for Lotronex.