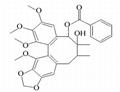
Gomisin C, a lignan first isolated from the fruits of S. chinensis, scavenges oxygen radicals and reduces the production of reactive oxygen species by inhibiting neutrophil activity. It has been shown to attenuate respiratory burst in rat peripheral neutrophils via suppression of NADPH oxidase (39% inhibition at 30 μg/ml) and inhibition of cytosolic calcium release from intracellular stores (36% inhibition at 50 μg/ml). Gomisin C can induce liver microsomal cytochrome P450, thus facilitating the clearance of xenobiotics and protecting against hepatotoxicity in rodent models of liver injury.