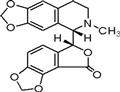
(+)-Bicuculline
- Product Name(+)-Bicuculline
- CAS485-49-4
- CBNumberCB3418662
- MFC20H17NO6
- MW367.35
- EINECS207-619-7
- MDL NumberMFCD00005006
- MOL File485-49-4.mol
Chemical Properties
| Melting point | 193-197 °C |
| alpha | D25 +130.5° (CHCl3) |
| Boiling point | 497.92°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.3694 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5600 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Benzene, Chloroform, DMSO, Ethyl Acetate |
| pka | 4.84(at 25℃) |
| form | Off-white to yellow powder. |
| color | Pale Yellow |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +126±6°, c = 1% in chloroform |
| λmax | 325nm(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,1203 |
| BRN | 98786 |
| InChI | 1S/C20H17NO6/c1-21-5-4-10-6-14-15(25-8-24-14)7-12(10)17(21)18-11-2-3-13-19(26-9-23-13)16(11)20(22)27-18/h2-3,6-7,17-18H,4-5,8-9H2,1H3/t17-,18+/m0/s1 |
| InChIKey | IYGYMKDQCDOMRE-ZWKOTPCHSA-N |
| SMILES | [H][C@]1(OC(=O)c2c3OCOc3ccc12)[C@@]4([H])N(C)CCc5cc6OCOc6cc45 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 485-49-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |
 
|
|||||||||
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H300+H310+H330-H400 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P260-P262-P273-P280-P302+P352+P310-P304+P340+P310 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T,N,Xn | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 23/24/25-50-36/37/38-20/21/22 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 36/37-45-61-36-26 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1544 6.1/PG 2 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | LV0909840 | |||||||||
| F | 10-23 | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1(b) | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29399990 | |||||||||
| Storage Class | 6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 very toxic hazardous materials | |||||||||
| Hazard Classifications | Acute Tox. 2 Dermal Acute Tox. 2 Inhalation Acute Tox. 2 Oral Aquatic Acute 1 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 ipr-mus: 8480 mg/kg CUTOEX 1,199,93 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704: |
|